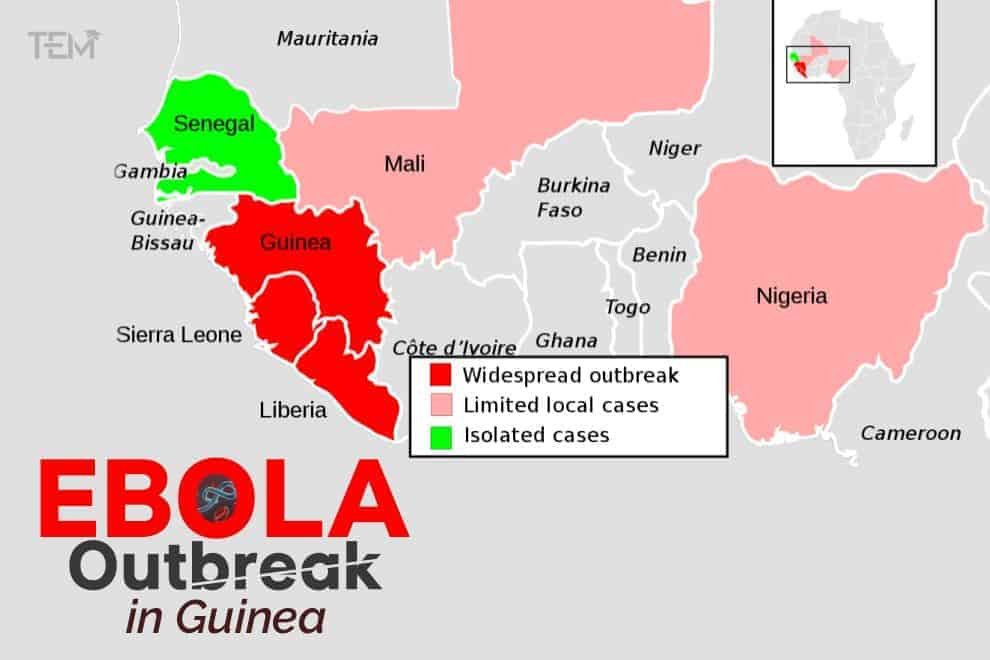
The government of Guinea has officially declared Ebola outbreaks on the 14th of February after a case was detected in the southeast of the West African nation. After 5 years of getting declared Ebola free, 3 people died in recent weeks from the virus and approximately 4 more people were confirmed to be infected with the virus.
The patients fell ill with vomiting, diarrhoea, and bleeding after attending a burial in Goueke sub-prefecture. Those who are still alive have been isolated in the treatment centres. On the 1st of February, the person buried was a nurse working at a health care centre, who died after being shifted to for treatment to Nzerekore city.
In the year 2013-2016 Ebola outbreak started in Nzerekore, in West Africa that caused over 11,300 deaths with a majority of cases in Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.
The Health Ministry of Guinea said in a statement, “Faced with this situation and in accordance with the international health regulations, the Guinea government declares an Ebola epidemic.” The ministry also said that the health workers have started to trace and isolate those who have been in contact with the Ebola-positive cases and will soon open a treatment centre in Goueke near Nzerekore city. The authorities have also asked the World Health Organization (WHO) for the new vaccines having better survival rates as compared to the previous one.
How Ebola outbreak Start?
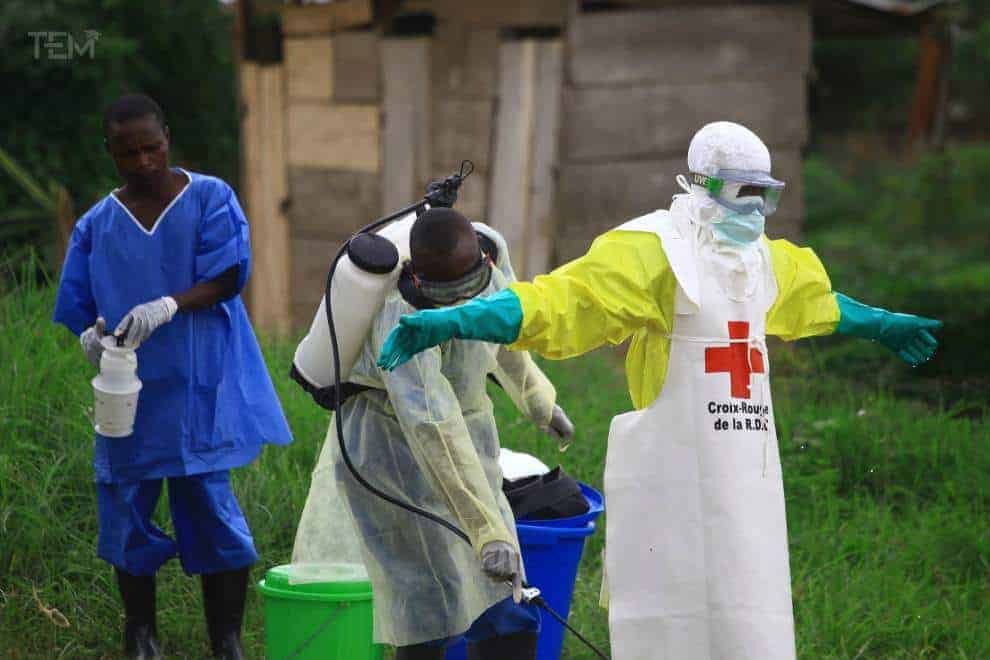

The nurse who died on the 28th of January near Nzerekore had a community funeral on the 1st of February, where people help wash the body is being considered as the major cause of an outbreak of the virus.
How Deadly is Ebola Virus?
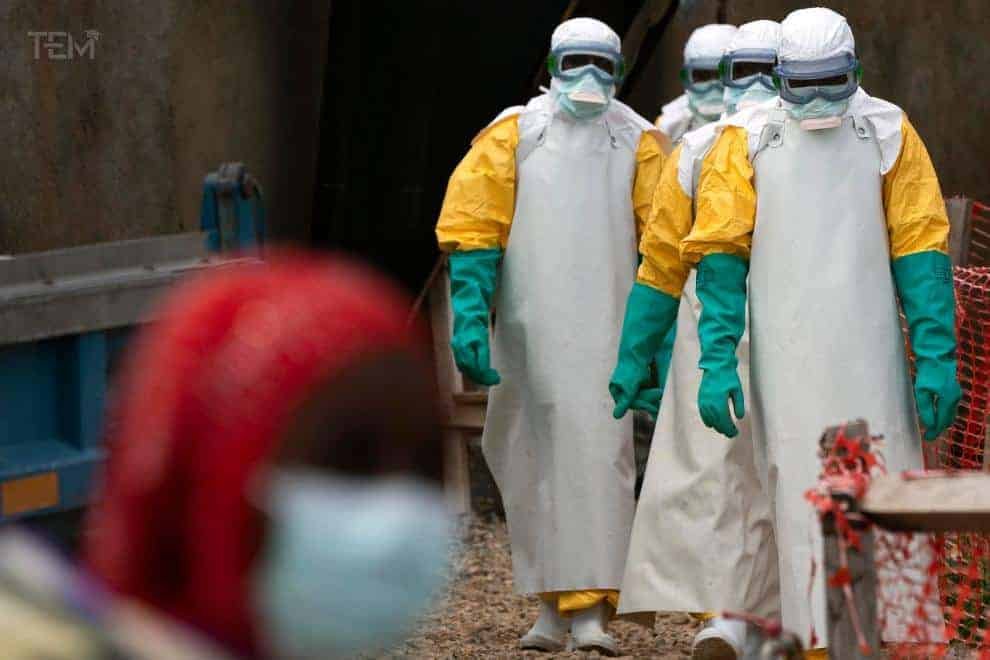

Ebola is one of the most deadly viruses or infectious diseases we know of. This deadly virus causes the death of approximately 50 percent of people who become infected. This virus disease is severe, often fatal illness, with a death rate of up to 90 percent.