Key Highlights:
- NASA will be launching baby squids and water bears to the International Space Station with SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket
- The creatures will be used to study tissue development and biological survival in space
- Additionally, NASA will also demonstrate the use of portable ultrasound in microgravity using Butterfly IQ Ultrasound
SpaceX’s Cargo Resupply Mission
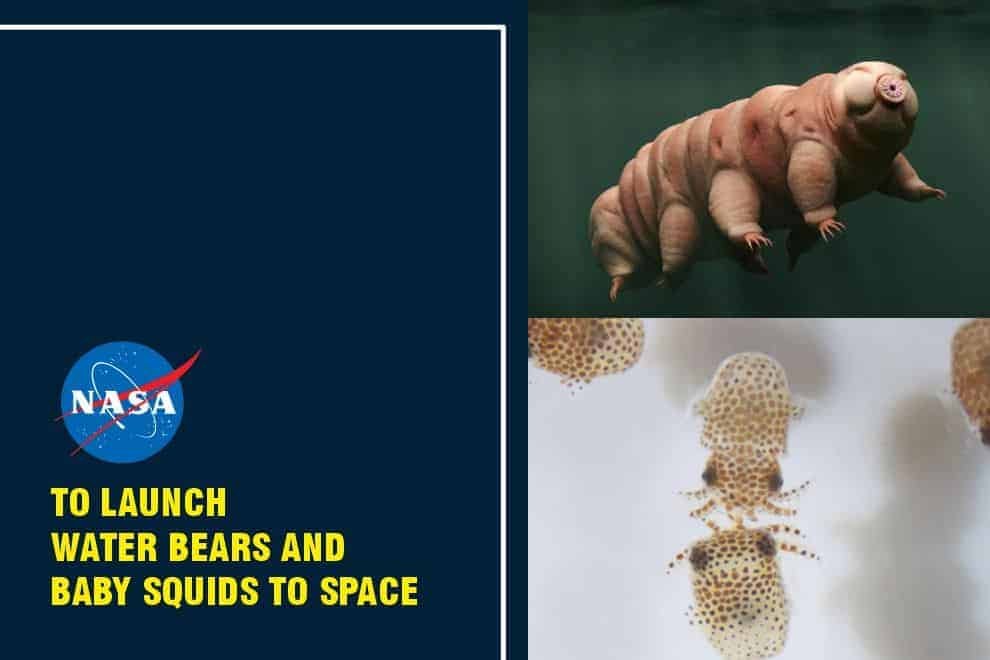
In its latest space advent, the American space agency NASA will be launching the most unexpected creatures to space. As part of SpaceX’s cargo resupply mission, the American space agency will be sending 5,000 tardigrades and 128 glow-in-the-dark baby squids to the International Space Station (ISS). SpaceX is scheduled to launch its 22nd mission to the space station on June 3, 2021, wherein it will carry supplies and scientific research and technology demonstrations from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, US.
The Unexpected Space Advent
In the upcoming mission, the SpaceX rocket Falcon 9 will be departing for the International Space Station with 5000 water bears and 128 glow-in-the-dark baby squids. According to a press release, NASA said that the 22nd SpaceX cargo resupply mission will carry equipment for scientific research and demonstrations. Apart from squids and water bears, the cargo resupply will also carry more than 7300 pounds of stuff that includes crew supplies, news solar panels, and vehicle hardware.
The take-off for the mission has been finalized from NASA’s Kennedy Space Centre in Florida. NASA said that the experiments aboard include studying how water bears tolerate space, whether microgravity affects symbiotic relationships, analyzing the formation of kidney stones, and more. It added that studying how space travel affects them will help scientists in understanding the impact of space travel on humans and coming up with countermeasures against the adverse effects of microgravity.
‘Water Bears’ and Glowing Squids
Otherwise known as water bears, Tardigrades, Hypsibius exemplaris, have been dubbed so due to their microscopic appearance. These are water habitats and are tiny in size. They can tolerate extreme environments that most life forms found on earth. They are not larger than 1.5mm and they are found everywhere from the depths of oceans to mountaintops. They can survive deadly radiation, extreme water, air deprivation, and starvation and they have already demonstrated their ability to get through space vacuum when they were last sent to space in September 2007.
Scientists will also be testing the glowing baby bobtail squids, Euprymna scolopes, which possess a special ability to grow because of the bacteria present inside them. NASA stated that the immune system of these creatures are similar to that of humans. They function in a symbiotic relationship, in a mutually codependent and coexisting environment. Scientists will be studying how their relationship is affected by space travel, which will guide them in mitigating the adverse effects on human’s symbiotic relationships with bacteria that live in our bodies.
Butterfly IQ Ultrasound and Other Studies
Additionally, scientists are also attempting to demonstrate the use of portable ultrasound in microgravity. The Butterfly IQ Ultrasound is a flight technology demonstration to test the functionality of novel technology in the spacecraft environment. The usability and autonomous operations of Butterfly IQ Ultrasound will be assessed for use in future human exploration missions beyond low-Earth orbit.
Meanwhile, Nasa will also undertake a study on kidney stones after some crew members exhibited increased susceptibility to kidney stones during flight. The Kidney Cells-02 investigation uses a 3D kidney cell model to study the effects of microgravity on the formation of microcrystals that can lead to kidney stones. “With this study, we hope to identify biomarkers or ‘signatures’ of cellular changes that occur during the formation of kidney stones,” Nasa quoted principal investigator Ed Kelly as saying.
Also Read:- Humans are the reason for climate change: NASA