A marine deposit fossil with three unique characteristics
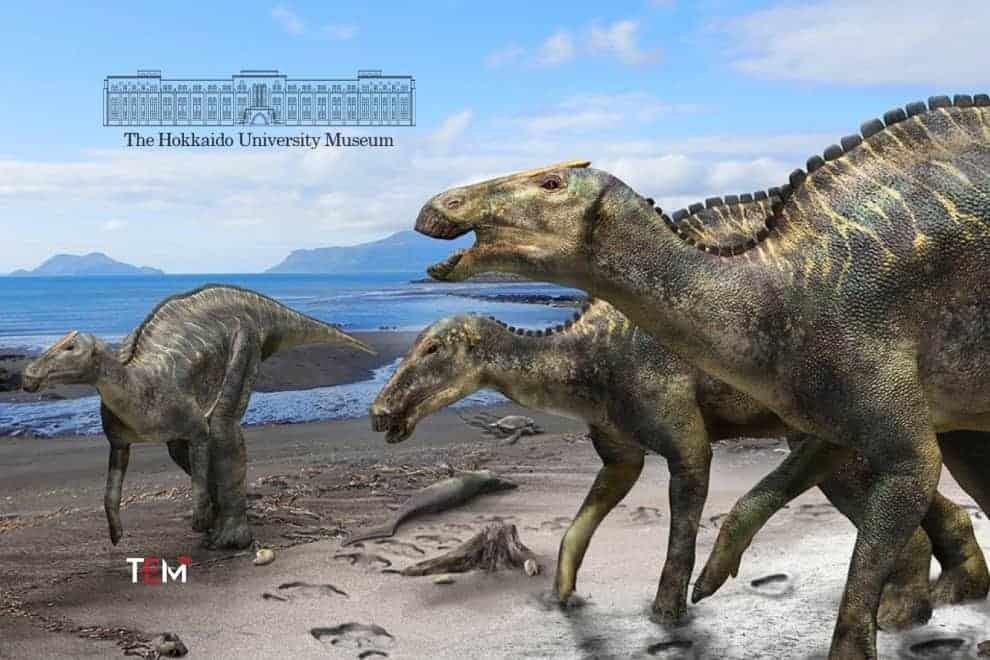
Fossils tell stories of dinosaur life richer than we have been willing to listen to. Archeologists often dust off some pre-historic facts from a dinosaur skeleton which bring wondering chaos in the mind of people. The recently discovered dinosaur fossil in Japan did the same. Nearly complete skeleton, the fossil was unearthed from 72 million-year-old marine deposits in Mukawa Town in Northern Japan. According to the study published in Scientific Reports, the fossil belongs to a new genus and species of an herbivorous hadrosaurid dinosaur. The scientists named the dinosaur Kamuysaurus japonicus.
A histological study done by Hokkaido University Museum found that the dinosaur was of age 9 years or older, measured 8 meters long and weighed between 4 tons to 5.3 tons. The frontal bone of its skull has a big articular facet connecting to the nasal bone, suggesting the dinosaur may have had a crest. The crest, if it existed, is believed to resemble the thin, flat crest of Brachylophosaurus subadults, whose fossils have been unearthed in North America.
Previous excavation
Earlier, in 2013, researchers have first discovered a partial tail of the same dinosaur in the outer shelf deposits of the Upper Cretaceous Hakobuchi Formation in the Hobetsu district of Mukawa Town, Hokkaido. Further excavations found a nearly complete skeleton that is considered as the largest dinosaur skeleton ever found in Japan. It’s been known as “Mukawaryu,” nicknamed after the excavation site, Mukawa.
Different from others, a deity dinosaur
A group of researchers led by Professor Yoshitsugu Kobayashi of the Hokkaido University Museum conducted comparative and phylogenetic analyses on 350 bones and 70 taxa of hadrosaurids. This current study led the discovery that the dinosaur belongs to the Edmontosaurini clade, which is closely related to Kerberosaurus unearthed in Russia and Laiyangosaurus found in China.
Further, the research team also found that the Kamuysaurus japonicus (the deity of Japanese dinosaurs) is very different from other dinosaurs in the Edmontosaurini clade. It has three unique characteristics: the low position of the cranial bone notch, the short ascending process of the jaw bone, and the anterior inclination of the neural spines of the sixth to twelfth dorsal vertebrae.
The study also brushes off revealing the origin of the Edmontosaurini clade and how it might have migrated from Asia and North America. And how they spread widely across what is now Alaska.
The possibility of migration
Team’s analysis pointed to the possibility that the ancestors of hadrosaurids and its subfamilies, Hadrosaurinae and Lambeosaurinae, preferred to inhabit areas near the ocean, suggesting the coastline environment was an important factor in the diversification of the hadrosaurids in its early evolution, especially in North America.
Also Read: Everything you need to know about human environment interaction